
What is the Glycemic Index of Quinoa? No Gluten
Glycemic Index Comparison. Quinoa has a lower glycemic index compared to most types of rice. This means that quinoa causes a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar levels compared to rice. Choosing quinoa over rice can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels.

Glycemic Load vs Glycemic Index Glycemic Load Table
Many research and review articles have been published on the nutritional and bioactive components of quinoa grains [18,19,20,21].However, only a few research articles on quinoa greens are available regarding their nutritional and phytochemical composition and human health benefits (Table 1).Furthermore, most research has been conducted in Europe and Asia, whereas only a few investigations have.

Red Quinoa GLYCEMIC INDEX based on test from Australia
The formula used for the GL calculation: the GI of the food x available carbohydrates per serving (g) / 100. A glycemic load value above 20 is considered high, while values in the range of 11 to 19 are considered medium. The glycemic index of quinoa is 53, and the glycemic load is 18. Moderate amounts of quinoa consumption can be recommended.

Quinoa GLYCEMIC INDEX based on test from Australia
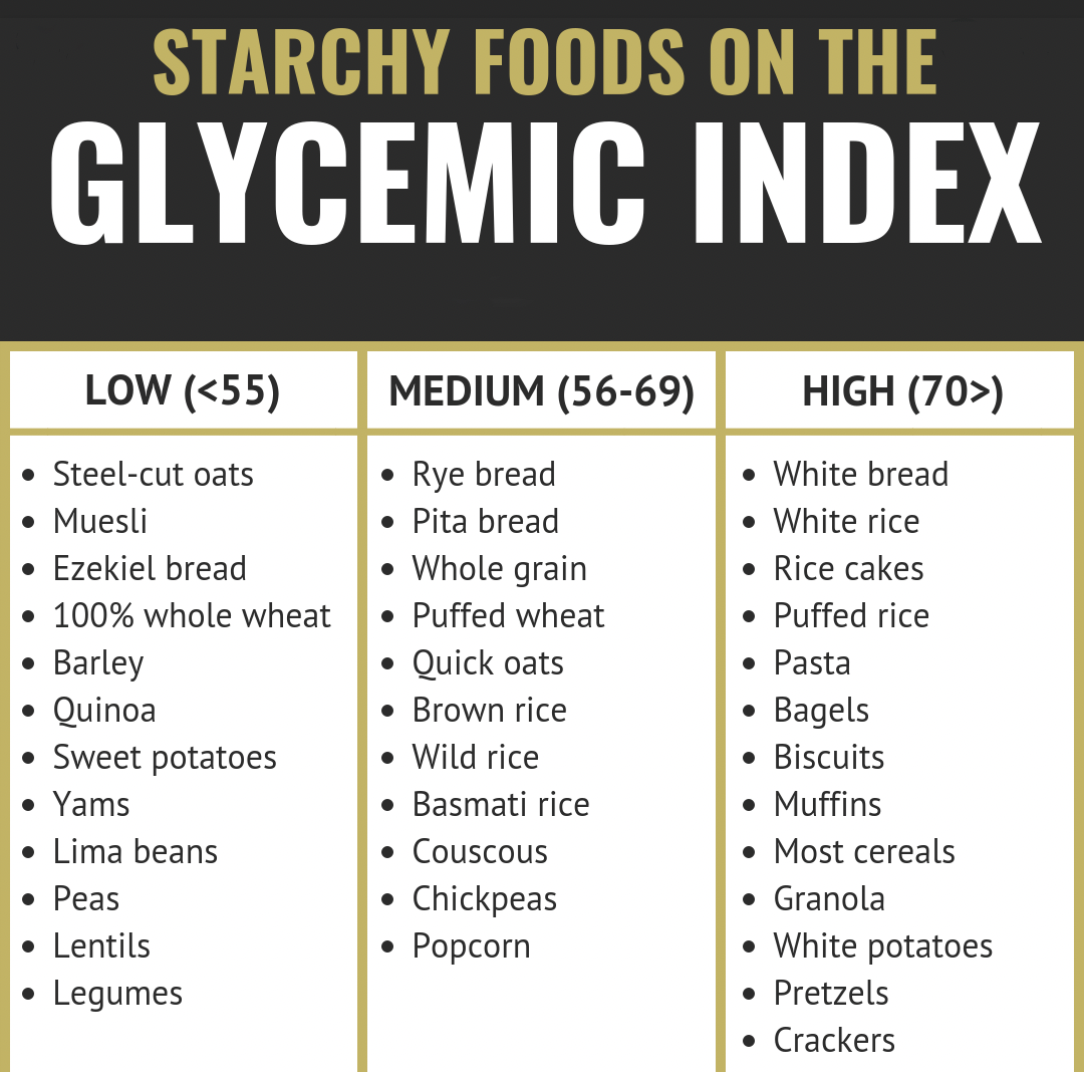
The GI (glycemic index) of quinoa is 53, which means it's a low-GI food. By comparison, the GI of white rice is roughly 73, while brown rice has a GI of 68. Potatoes have a high GI because they contain starch; their average value is 78 grams per 100 grams (g/100g). Pasta averages between 43-61 g/100g, and whole grain bread are usually 74 g/100g.

(PDF) Glycemic index profiling of germinated quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa wild)
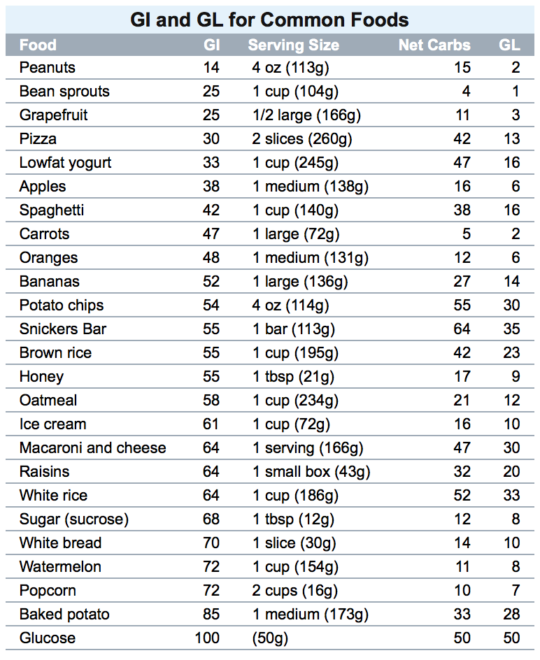
Though there are around 120 different varieties of quinoa available today, the most popular and commonly sold types are red, white and black quinoa. This product has an average glycemic index of 53, based on a 150-gram serving or 1 cup of freshly cooked quinoa. The portion also contains 32 grams of carbohydrates and 1 gram of sugar.

glycemic index quinoa
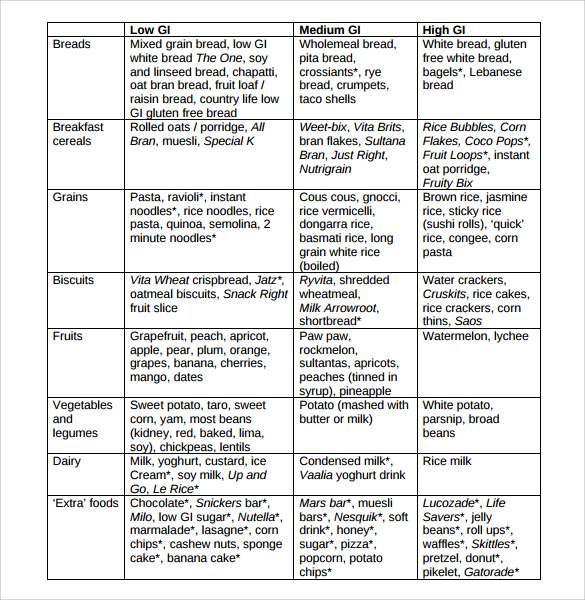
Low glycemic index (GI of 55 or less): Most fruits and vegetables, beans, minimally processed grains, pasta, low-fat dairy foods, and nuts. Moderate glycemic index (GI 56 to 69): White and sweet potatoes, corn, white rice, couscous, breakfast cereals such as Cream of Wheat and Mini Wheats. High glycemic index (GI of 70 or higher): White bread.

Quinoa & the Glycemic Index
Quinoa is a healthy pseudocereal that is much more nutritious than other cereal products. A new Nutrients journal study reports the ability of quinoa to normalize glucose metabolism in the body.
Quinoa Diabetes Glycemic Index DiabetesWalls
Quinoa and the Glycemic Index. The glycemic index, or GI, is a rating system that shows the impact of carbohydrate-containing foods on blood sugar compared to pure glucose. Glucose, which significantly spikes blood sugar, has a GI score of 100. Using a scale of zero to 100, GI scores are separated into three groups — low, moderate, and high.

Glycemic Index Profiling of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) Variety Semantic Scholar
Low-glycemic foods are always recommended as they have a good amount of fiber. A serving size of 150 grams of quinoa contains approximately 32 grams of carbs (that includes 1 gram of sugar) rates a 53 on the GI. This is not the lowest level you can get, but it does place the grain firmly into the lower region of the glycemic index.

Glycemic index and glycemic load of germinated quinoa Download Table
Dietary fibers help adjust a person's blood sugar, because they ferment in the colon rather than undergo digestion in the small intestine. Quinoa contains 2.1 g of fiber per 100 g, whereas white.

glycemic index quinoa
Quinoa Glycemic Index: A Guide to Healthy Eating Introduction to Quinoa and Glycemic Index. As someone who's deeply passionate about health and wellness, I've often explored various foods and their impacts on our health. In this journey, I've come across quinoa, a superfood that's gained immense popularity lately. But what makes quinoa.

glycemic index quinoa
The glycemic load (GL) of quinoa is equal to 7.3, which classifies it as a low GL food. 100 grams of quinoa (cooked) contain 120 kcal (502 kJ), 4.4 grams of proteins, 21.0 grams of carbohydrates, and 1.9 grams of fats. Quinoa is a nutritious grain that has gained popularity in recent years due to its high protein and fiber content.

Learn why quinoa is a superfood. Quinoa health benefits, Quinoa benefits, How to eat better
But not all carbs are equal. Quinoa is considered a whole grain, which is better for you than refined grains like white flour. Quinoa has a glycemic index of 53, which is a measure of how quickly.

Glycemic index quinoa
Quinoa shines in the glycemic arena. With a low to moderate GI ranging from 53 to 68, it boasts a slower and more gradual impact on blood sugar levels. The glycemic load of quinoa is also relatively low, indicating that it can be a sensible choice for individuals mindful of their blood sugar.
FREE 7+ Sample Glycemic Index Chart Templates in PDF
This means that quinoa can be particularly beneficial for people with diabetes, since fiber and protein are considered important for keeping blood sugar under control. Managing total carbohydrate.
Quinoa Vs Rice Is Quinoa Really Better Than Rice? Wirally
A Quinoa (főtt) 100 grammjának átlagos kalóriatartalma 120 kcal, fehérjetartalma 4.4 gramm, zsírtartalma: 1.9 gramm, szénhidráttartalma (ch tartalma) 18.5 gramm. A szénhidráttartalom az oldalon esetenként ch, ill. ch tartalom rövidítéssel szerepel. Az oldalon szereplő valamennyi adat ellenőrzött és hiteles forrásból számazik.